This website provides a simple, step by step, chronological look at the development of the Dorso-Ventral (D-V) axis in the Xenopus egg.
- Navigation bars are located to the left of the page and are orgnised chronologically from top to bottom.
- Associated images are labelled as such (Fig I) and referenced in acompanying text.
- All text highlighted in bold is defined in the glossary page which is accessable via the navigation bar.
- All images were created by one of this websites creators, Neal Rimmer and permission is given for use in this website alone.
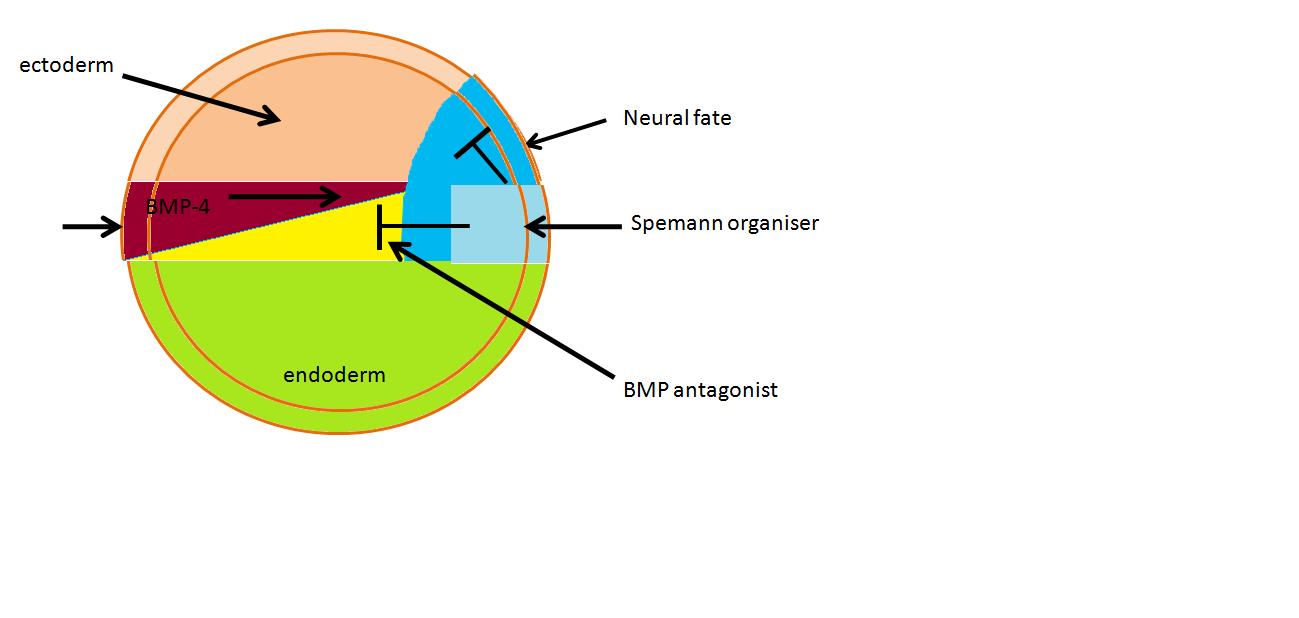
Notation FIG I.
The following diagram illustrates the accepted notation for regions of the blastula.
Overview
- Sperm enters the egg, the point of entry is destined to become the ventral pole of the egg.
- The nerwly fertilised egg undergoes a 'cortical rotation' localising dorsalising factors to the Dorso-Vegetal region.
- Meanwhile, VegT induces Vg1 at the vegetal pole, which induces expression of TGFβ signalling ligand Nodal.
- Cells which recive intermediate concentrations of Nodal differentiate into a band of mesoderm around the equator of the blastula.